Understanding Tourism Satellite Accounts: A Comprehensive Guide
Tourism is a critical sector for many economies worldwide, influencing job creation, economic growth, and cultural exchange. However, measuring the full economic impact of tourism can be complex. This is where the Tourism Satellite Account (TSA) comes into play. In this blog, we’ll explore what a TSA is, its significance, and how it helps in understanding the economic contributions of tourism.
What is a Tourism Satellite Account (TSA)?
A Tourism Satellite Account is a standardized framework developed by the United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO), the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), and the European Union (EU) to measure the economic impact of tourism on a country’s economy. It complements the System of National Accounts (SNA) by providing detailed data on tourism’s contribution to GDP, employment, investment, and trade.
Key Components of a Tourism Satellite Account
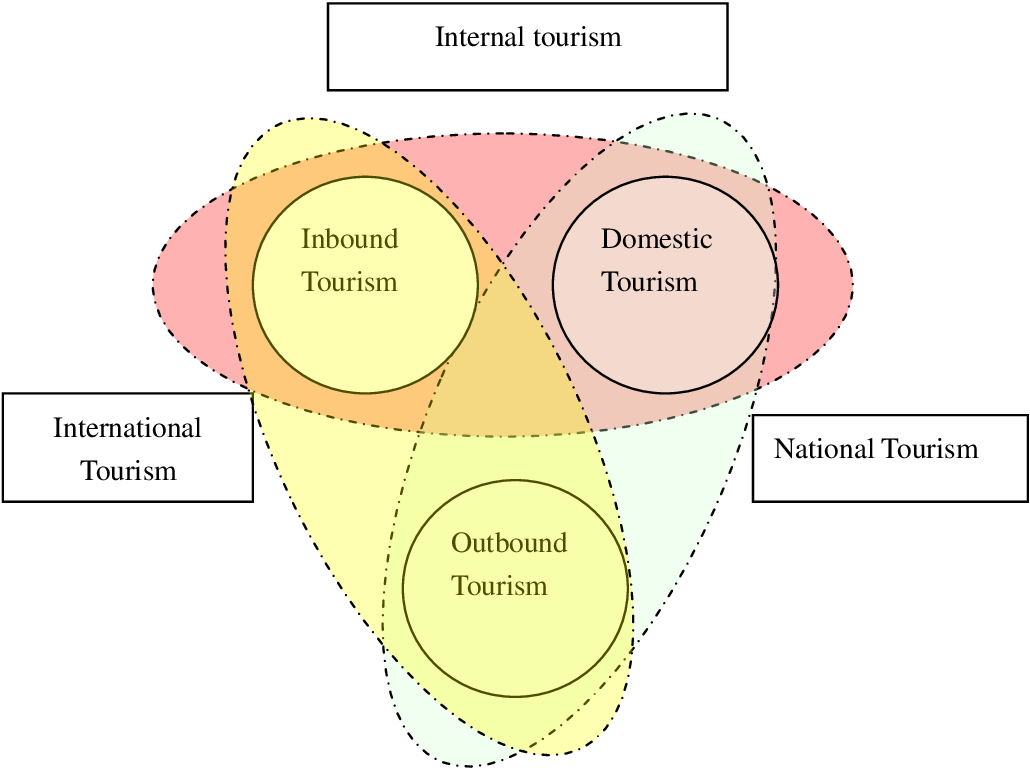
- Tourism Consumption: This includes all expenditures made by visitors for and during their trips, covering both inbound (international tourists) and domestic (local tourists) tourism.
- Tourism Supply: The production of goods and services to meet the demands of tourists. This covers industries such as accommodation, food and beverage services, transportation, entertainment, and cultural services.
- Value Added of Tourism Industries: This measures the difference between the output of tourism-related industries and the intermediate consumption (the cost of goods and services used to produce the output).
- Employment in Tourism Industries: Provides data on the number of jobs generated by tourism activities, both directly (e.g., jobs in hotels, restaurants, and travel agencies) and indirectly (e.g., jobs in supply industries).
- Gross Fixed Capital Formation: Investments made in tourism-related infrastructure and facilities, such as hotels, airports, and recreational facilities.
- Tourism Trade: Exports and imports of tourism-related goods and services, showing the balance of payments related to tourism.
The Importance of Tourism Satellite Accounts
- Economic Planning and Policy Making
- Informed Decisions: TSAs provide governments with detailed data to make informed decisions about tourism policies and strategies.
- Resource Allocation: Helps in the efficient allocation of resources towards sectors that significantly contribute to economic growth through tourism.
- Investment and Development
- Infrastructure Development: By understanding tourism’s economic impact, governments and private investors can prioritize investments in tourism infrastructure, such as airports, hotels, and cultural sites.
- Sustainable Tourism: TSAs help in developing policies that promote sustainable tourism practices, balancing economic benefits with environmental and cultural preservation.
- Employment and Job Creation
- Job Market Insights: Detailed employment data from TSAs highlight the significance of tourism in job creation, aiding in workforce development and training programs.
- Economic Opportunities: Helps identify areas with high employment potential within the tourism sector, supporting job creation and economic opportunities for local communities.
- Performance Monitoring
- Trend Analysis: TSAs allow for the monitoring of tourism trends over time, helping to assess the effectiveness of tourism policies and strategies.
- Benchmarking: Countries can compare their tourism performance with international standards and best practices, driving improvements and competitiveness.
- Understanding Economic Linkages
- Inter-Industry Relations: TSAs highlight the linkages between tourism and other economic sectors, demonstrating the multiplier effect of tourism on the broader economy.
- Supply Chain Management: Provides insights into the tourism supply chain, helping businesses optimize their operations and collaborations.
How to Develop a Tourism Satellite Account
- Data Collection
- Surveys and Statistics: Collect data from various sources, including visitor surveys, business surveys, and national statistics.
- Administrative Records: Use data from immigration records, transportation departments, and financial institutions.
- Data Integration
- Harmonization: Integrate data from different sources into a coherent framework, ensuring consistency with national accounts.
- Categorization: Classify data according to standard tourism categories (accommodation, food services, transportation, etc.).
- Compilation and Analysis
- Statistical Techniques: Apply statistical methods to estimate the economic variables related to tourism.
- Economic Modeling: Use economic models to analyze the relationships between tourism and other sectors of the economy.
- Reporting and Dissemination
- Publications: Produce comprehensive reports and publications detailing the findings of the TSA.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Share the results with government agencies, industry stakeholders, and the public to inform policy and business decisions.
Challenges in Implementing TSAs
- Data Availability and Quality
- Comprehensive Data: Ensuring the availability of high-quality, detailed data can be challenging, especially in countries with limited statistical infrastructure.
- Timeliness: Collecting and processing data in a timely manner is crucial for accurate and relevant TSA results.
- Methodological Consistency
- Standardization: Ensuring methodological consistency across different regions and over time is essential for reliable comparisons.
- Training and Expertise: Developing TSAs requires specialized skills and knowledge, necessitating training and capacity building.
- Resource Constraints
- Funding: Adequate funding is necessary to support the extensive data collection and analysis required for TSAs.
- Technical Resources: Access to advanced statistical tools and technologies is vital for the efficient compilation and analysis of TSA data.
Conclusion
Tourism Satellite Accounts are invaluable tools for understanding the comprehensive economic impact of tourism. They provide detailed insights that help governments, businesses, and communities make informed decisions, drive investment, create jobs, and promote sustainable tourism development. Despite the challenges in implementation, the benefits of developing and maintaining a TSA far outweigh the difficulties, making it a crucial component of national economic planning and policy-making.
For more information;www.paktoursntravel.com